
World First Most Comprehensive AI 3D Medical Collections. Powered by Grafile
Grafile is the resource designer and developer for Software Companies, Media, Education, Publisher and more..


$811.00
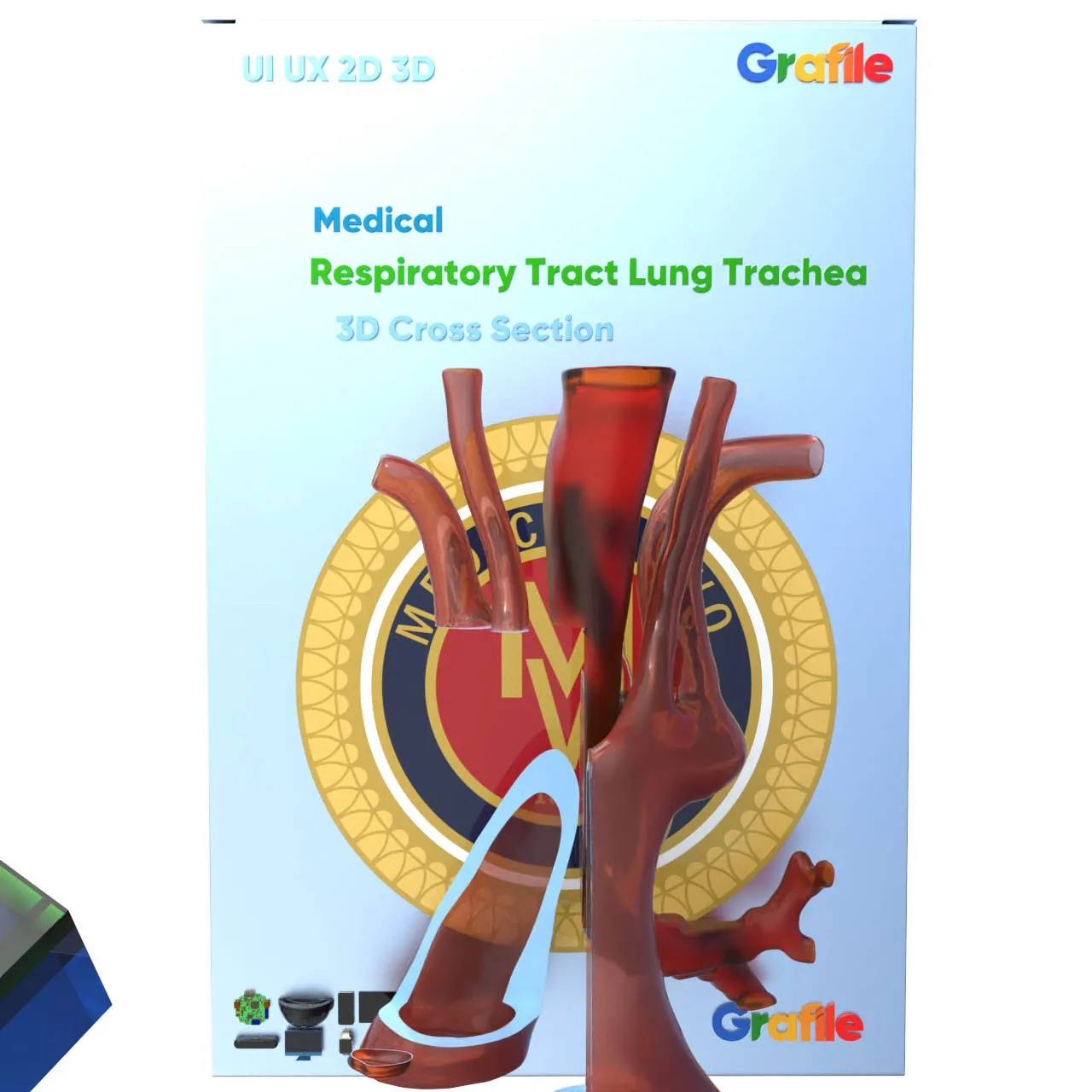
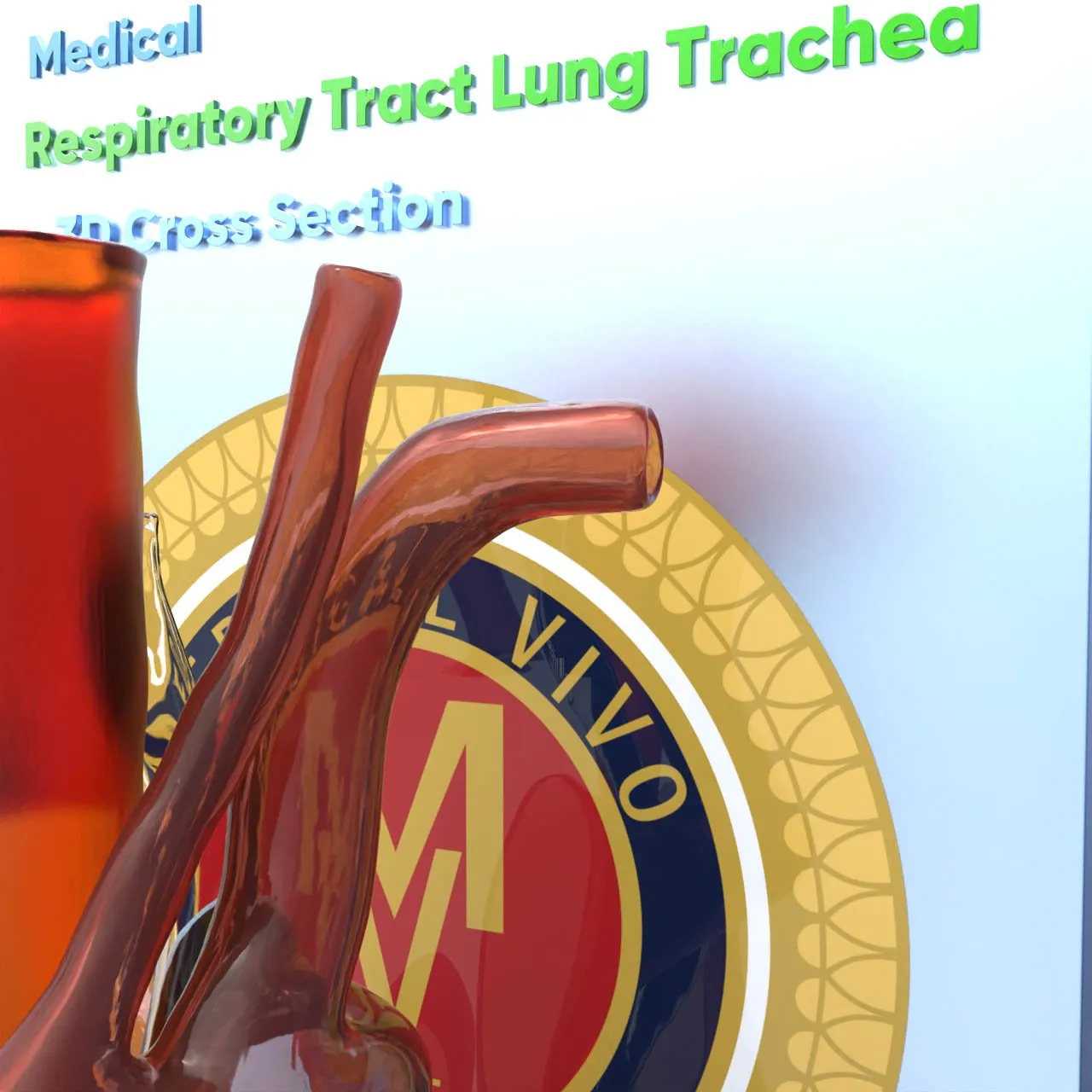
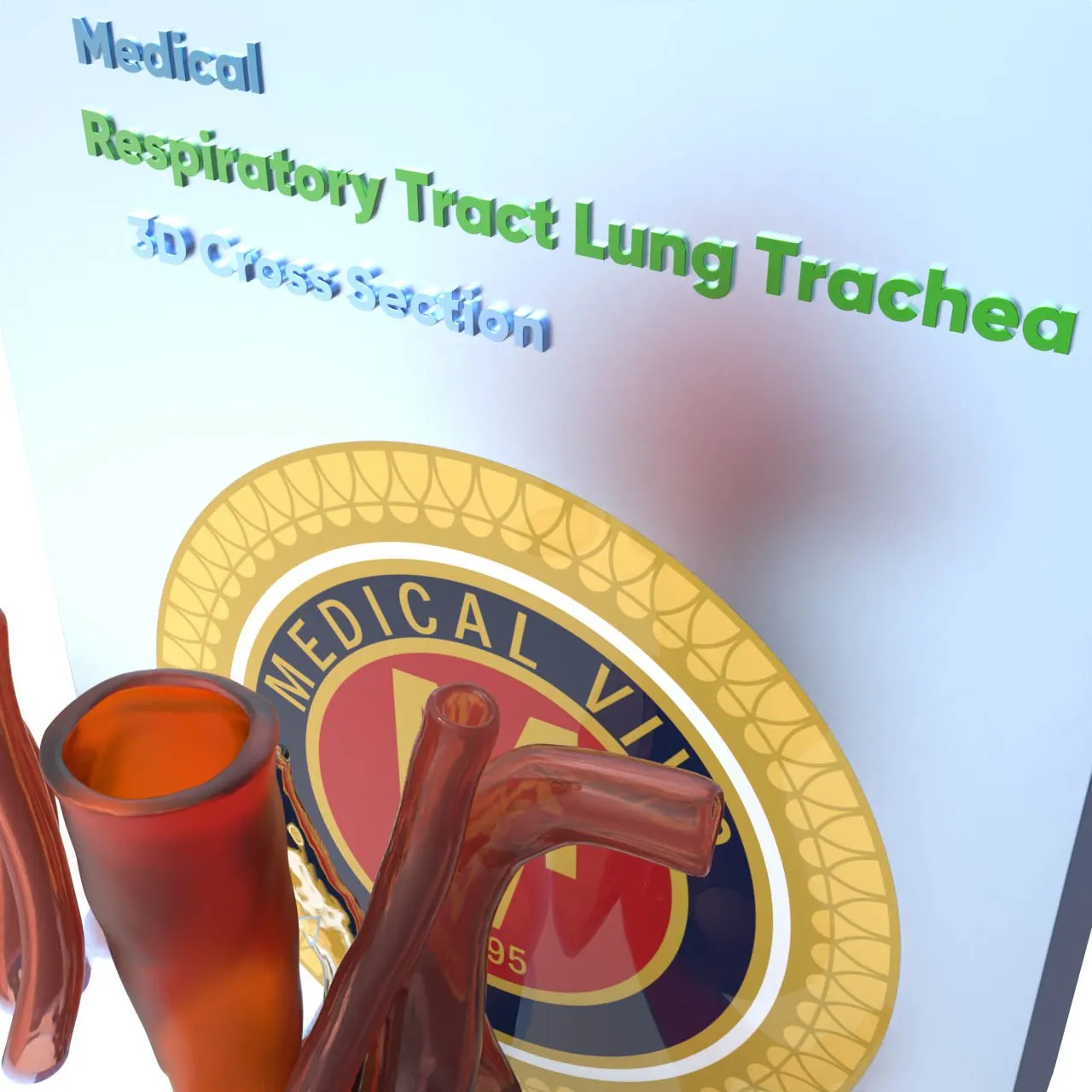
The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe, is a vital component of the respiratory system. It is a tube that connects the larynx (voice box) to the bronchi, which lead into the lungs.
Medical Education and Specialist Doctors and Pharmacists, Dentistry, Pharmacy, Nutrition, Nursing, Pharmacology, Physiotherapy and other related medical professionals.
Hospitals, Clinics, Colleges and Universities that provide Medical Education.
Businesses in the Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Sector.
Software Companies, Game, Film and TV Industry
Broadcast and Live Events
The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe, is a vital component of the respiratory system. It is a tube that connects the larynx (voice box) to the bronchi, which lead into the lungs. Here are some key points about the trachea:
![]()
| Brand | Medical, Medical 3D, Medical Education, Medical R&D |
|---|

World First Most Comprehensive AI 3D Medical Collections. Powered by Grafile
Grafile is the resource designer and developer for Software Companies, Media, Education, Publisher and more..
All files are transmitted in securely encrypted packages, organized by Designs and Software.
Files are dispatched within 24 hours on business days following the order date.
For weekends and holidays, dispatch occurs within 48 hours.
To assist you in reducing your long-term costs, we have established a Subscription Service. This service ensures that you have access to the latest versions of our icons. With our Products, you will receive all new product releases automatically over a 12-month period.
To keep you at the forefront of design, Grafile Icon Collections provides a Comprehensive Service. This service ensures that you receive the latest versions of their icons for an entire year, with new product launches conveniently sent to you. Personalized Icons Designed for You Should you need a particular icon that is not included in our collection, please feel free to reach out. We value your input; simply click here to fill out our suggestion form.
We are a team of professional software developers actively engaged in partnerships with industry leaders such as Intel, Microsoft, and the Visual Studio Marketplace. It is crucial to concentrate on project execution without getting sidetracked by design tools. Grafile designs offer insights into the fundamental requirements of your project, as they are utilized by some of the world's foremost software companies, particularly Microsoft. These designs inspire innovative development ideas.
The Grafile Design Collections encompass a wide array of designs employed by major corporations like Microsoft, Apple, Samsung, and GE. They feature designs that are fully aligned with the optimal User Interface specifications for your application. If you are working on a specialized project, we can swiftly address your unique design requirements without any additional cost. By utilizing familiar icons recognized by Windows, MS Office, Mac, and Android users in appropriate contexts, you can streamline your user training processes and enhance the likelihood of your program's sales success.
In our quest for optimal efficiency, we have expertly reduced the file sizes of Illustrator documents. Our meticulous optimization process has resulted in a reduction of anchor points, the creation of axis-aligned paths, and the establishment of fixed closure points. We have eliminated superfluous elements by correcting unnecessary handles and removing unused swatches, brushes, and symbols, providing you with a streamlined and uncluttered canvas for your creative projects.
Our designs feature the smallest possible dimensions and the fewest anchor points. By utilizing grade, your project dimensions can be kept to a minimum. To avoid unnecessary memory leaks and numerous media errors that are not attributable to you during project execution, consider using Grafile collections.
Every design within Grafile is meticulously crafted. Aspects such as color, alignment, adornment usage, directions, angles, and margins are fully aligned with Microsoft Design Guidelines.
You will find graphic collections that closely align with your Notation in Java, C#, C++, or any other programming language. This allows you to utilize them without wasting time on compatibility and accuracy checks, as Microsoft is a Grafile customer. Additionally, Grafile is accessible on the Visual Studio Marketplace.
Incorporate Grafile into your projects to gain a competitive edge.
If you require particular additional icons, please do not hesitate to reach out to us with your suggestions. Click here to access the suggestion form.
Each purchase package includes up to 100 complimentary icons tailored for your project.
As software developers, we understand the value of time, and we strive to create additional designs promptly.
For requests exceeding 100 icons, we ensure delivery in the shortest timeframe possible, offering competitive pricing.
Our collaboration with Microsoft is showcased below, highlighting the importance we place on our partnership with you and the product development process.
Our team purchased Bonus Vista icon Presentation from you and are now facing a dilemma. We now have over 4000 icon files and now way to preview them, unless I open them all separately. That said, do you guys have a spreadsheet or some visual representation of the icons with file names in this pack? Or do you have a XAML Icon Previewer that I can download?
These are really great icons! I am frustrated spending SO much time looking for the right one…and need some help!
Thanks in advance!
Pam Scott
User Experience Designer | RXD
Microsoft IT
Hi,
We have discussed your recquest with our software developers team.
They can complete developing the XAML Viewer program in 2-3 days.
Please note that this product is intended for your internal use only.
It will not be for sale.
Thank you.
We completed xaml viewer project before 2 days,
we will fix bugs soon
Xaml viewer Beta 1.0 ready for download,
Free software its for preview xaml files
Organize your xaml files
Build Resource dictionaries from xaml files
Edit Resource dictionaries
Update Resource dictionaries
Ok…this is a very cool little tool! In case you care, here is a list of things I love!
- Keeps your common XAML folders in memory
- Searches in my saved folders – hot!
- Nice preview with zoom feature…HELLO!!
- Easy to use, no training necessary
- I love the dictionary feature…life is good now.
You guys rock! You took my simple request and made a product that meets more of my needs than I thought I had!
Thanks so much…again!
No account yet?
Create an Account